
Have you ever collected vinyl records, limited edition prints, or kept ticket stubs from memorable events? If so, you already understand the basic concept behind NFTs! Let’s explore this digital innovation in straightforward, accessible terms.
What Does NFT Stand For?
NFT stands for “Non-Fungible Token.” Simply put, this means “a unique digital item that cannot be replaced with something else.”
Let’s break this down with a practical example:
Fungible means something can be exchanged for an identical item with no difference in value. Consider a $20 bill. If you and a friend exchange $20 bills, neither of you will care which bill you have because they’re functionally identical.
Non-fungible means something is unique and cannot be equally exchanged. Your first-edition signed book might look similar to other copies, but its signature and specific history make it irreplaceable and uniquely valuable. That’s non-fungible!

NFTs Explained Using Everyday Examples
Currency vs. Property Deeds
Think about the difference between money in your bank account and the deed to your home:
- Money is fungible – a dollar in your account is worth exactly the same as any other dollar.
- A property deed is non-fungible – it represents ownership of a specific piece of real estate with unique characteristics, location, and value.
NFTs function like digital property deeds – each one represents ownership of something specific and unique.
Mass-Produced Items vs. Collectibles
Consider another comparison:
- Generic products are fungible – one standard iPhone 15 is functionally identical to another of the same model.
- Collectibles are non-fungible – a vintage watch, rare whiskey bottle, or first-edition book has unique properties that affect its value.
NFTs operate like digital collectibles, each with its own distinctive characteristics and provenance.
What Makes NFTs Special?
NFTs have several distinctive features that differentiate them from physical collectibles:
1. Blockchain-Based Verification
NFTs exist on blockchain technology – essentially a decentralized digital ledger that publicly records ownership. This provides transparency and verification that can’t be altered.
Imagine a public record of ownership that isn’t controlled by any single organization or government. When you own an NFT, that ownership is recorded on the blockchain where it’s visible to anyone and extremely difficult to dispute or forge.
2. They Extended Beyond Visual Art
While digital artwork dominates the NFT conversation, they can represent:
- Music and audio recordings
- Videos and animations
- Virtual real estate in digital worlds
- Event tickets and membership passes
- Interactive experiences
- Digital fashion and wearables
- Domain names
- And many other digital assets
3. Verifiable Authenticity in a Copy-Paste World
In a digital environment where perfect copies are made with a simple right-click, NFTs establish verifiable ownership and authenticity.
Think of it like this: Anyone can download an image of the Mona Lisa, but only the Louvre owns the original. With NFTs, the blockchain serves as a public certificate of authenticity and ownership, clearly distinguishing the original from any copies.
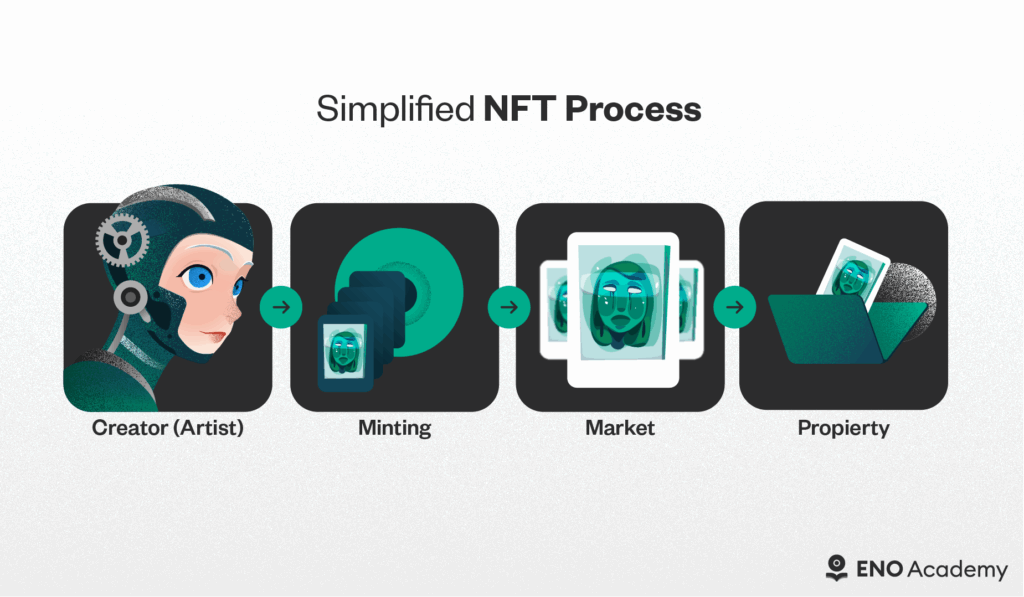
How Do NFTs Work? The Straightforward Version
Let’s walk through the NFT process in simple terms:
Creating (Minting) an NFT
Create digital content – artwork, music, video, or other digital asset
- Connect to an NFT marketplace – platforms like ENO Marketplace provide the tools to turn your creation into an NFT
- Mint your NFT – this process records your creation on the blockchain with a unique identifier
- Set your terms – establish the price, royalties for future sales, and other details
Buying and Selling NFTs
Marketplace transactions – NFTs are typically bought and sold on specialized platforms
- Cryptocurrency payment – most NFT purchases use cryptocurrencies like Ethereum
- Blockchain transfer – when a sale occurs, the blockchain record updates to show the new owner
- Creator royalties – many NFTs include automatic royalty payments to the original creator whenever the NFT is resold
Why Do People Buy NFTs?
People acquire NFTs for various reasons:
- Collection and appreciation – just as with physical art or collectibles
- Supporting creators – direct financial support for artists and content creators
- Investment potential – speculation on future value increases
- Utility and access – some NFTs provide exclusive benefits, access, or functionality
- Digital identity and status – displaying digital assets in virtual environments
Common Questions About NFTs
"If anyone can view or copy the digital asset, what´s the value of owning the NFT?"
While anyone can view or download a copy of the digital asset, only the NFT owner possesses the verifiable “original” as recorded on the blockchain. This distinction creates value, similar to how anyone can buy a poster of a famous painting, but only one person or institution owns the original.
"Are NFTs enviromentally sustainable?"
Early NFT technology, particularly on the Ethereum blockchain, consumed significant energy. However, newer platforms (including what ENO uses) have dramatically reduced energy consumption through more efficient consensus mechanisms, making them far more environmentally sustainable.
"How do I know if an NFT is a good investment?"
Like any investment, research is essential. Consider the creator’s reputation, the project’s roadmap, the community around it, and whether you personally value the asset beyond potential financial returns. Never invest more than you can afford to lose, especially in such a new and volatile market.
NFTs and Digital Ownership: Why It Matters
Before NFTs, true ownership of digital assets was problematic. Streaming a movie or downloading music typically meant purchasing a license to access content, not actually owning it.
NFTs represent a paradigm shift in digital ownership. They establish a clear record of who owns what in the digital realm, enabling new economic models and opportunities for creators and collectors alike.
Consider professional photographers who previously struggled to monetize their work in an age of endless digital reproduction. With NFTs, they can sell authentic, verifiable originals while maintaining copyright and earning royalties on future sales
Key NFT Terminology Simplified
Understanding these basic terms will help navigate the NFT ecosystem:
- Minting: The process of creating a new NFT and recording it on the blockchain
- Wallet: Digital software that stores your NFTs and cryptocurrencies
- Gas fees: Transaction costs for performing actions on the blockchain
- Smart contract: Self-executing code that automatically implements the terms of an agreement
- Blockchain: The distributed ledger technology that records NFT ownership
- Cryptocurrency: Digital currency used to purchase NFTs
- Royalties: Automatic payments to the original creator when an NFT is resold
Navigating NFT Security
As with any valuable assets, security precautions are essential:
- Protect your wallet credentials – never share your private keys or recovery phrase
- Use strong, unique passwords and two-factor authentication
- Research thoroughly before purchasing – verify creator authenticity and project legitimacy
- Start conservatively – limit initial investments until you’re comfortable with the process
- Beware of phishing attempts – verify marketplace URLs and be cautious of unsolicited offers
The Future of NFTs: Practical Applications
While much attention focuses on digital art and collectibles, NFTs have broader potential applications:
- Legal documents: Deeds, certificates, and credentials that cannot be falsified
- Ticketing: Event tickets that eliminate scalping and counterfeiting
- Intellectual property: Clear tracking of creative rights and licensing
- Supply chain verification: Authenticating products from manufacturer to consumer
- Identity verification: Secure, privacy-preserving digital identity solutions
- Fractional ownership: Making expensive assets accessible through partial ownership tokens

ENO: Making NFTs Accessible for Everyone
Now that you understand what NFTs are, let’s introduce ENO – a platform designed to make NFT creation and collection accessible to everyone, regardless of technical expertise.
ENO stands out by addressing common barriers to NFT participation:
- Intuitive user experience: ENO’s platform requires no prior blockchain experience
- Creator-focused tools: Simple yet powerful features help creators monetize their work
- Cost-effective technology: ENO uses Layer 2 solutions on Arbitrum to minimize transaction fees
- Educational resources: ENO Academy provides comprehensive learning materials for beginners
- Intelligent assistance: Agnes AI offers personalized recommendations and market insights
Whether you’re a creator looking to monetize your digital work or a collector interested in supporting artists and owning unique digital assets, ENO provides an accessible entry point to the NFT ecosystem.
Conclusion: NFTs Represent a New Frontier of Digital Ownership
NFTs are fundamentally changing our concept of ownership in the digital realm. They create scarcity and verifiable authenticity in a world where digital content can be infinitely copied. While the technology behind them involves complex cryptography and blockchain systems, the core concept is straightforward – they establish clear, public records of who owns unique digital assets.
As our lives become increasingly digital, understanding concepts like NFTs becomes more relevant. Whether you’re interested as a creator, collector, investor, or simply a curious observer, NFTs represent an important evolution in how we value and exchange digital goods.
Ready to explore further? Visit ENO Academy to continue your NFT journey with comprehensive resources designed for beginners at any age.
This article is part of ENO’s educational series for Web3 beginners. Our mission is to make the exciting world of digital assets accessible to everyone through clear explanations and user-friendly tools.






